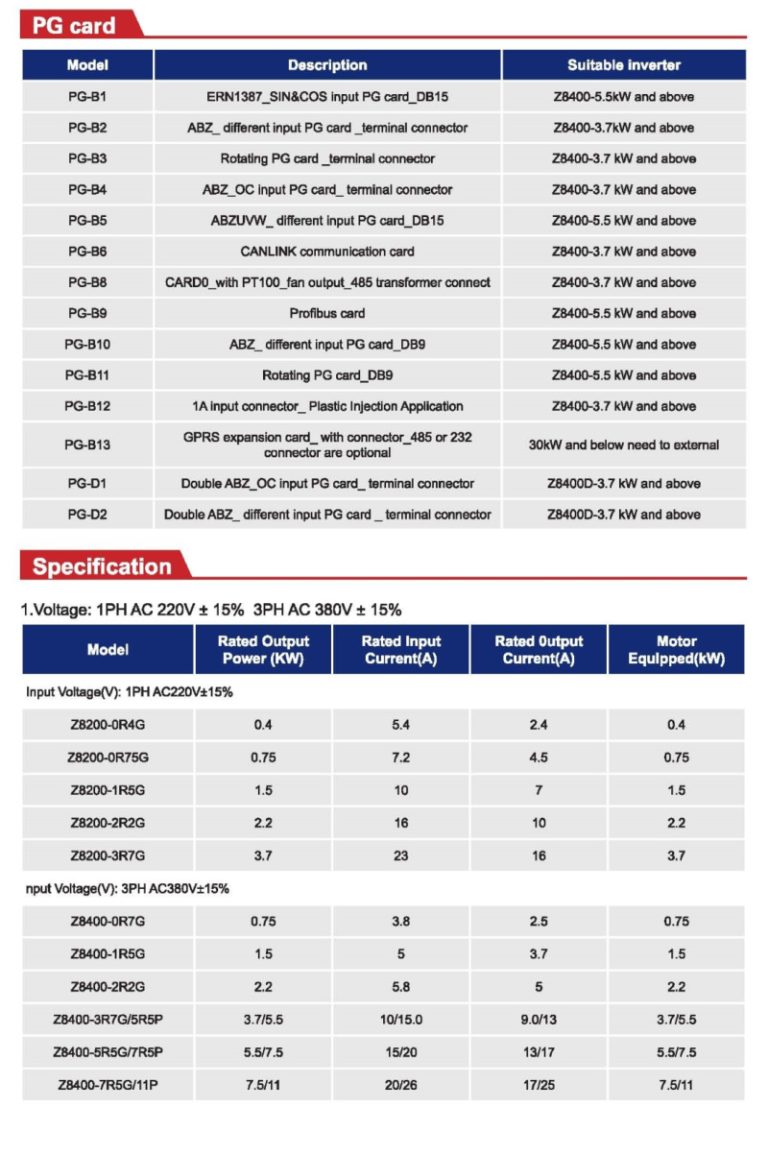
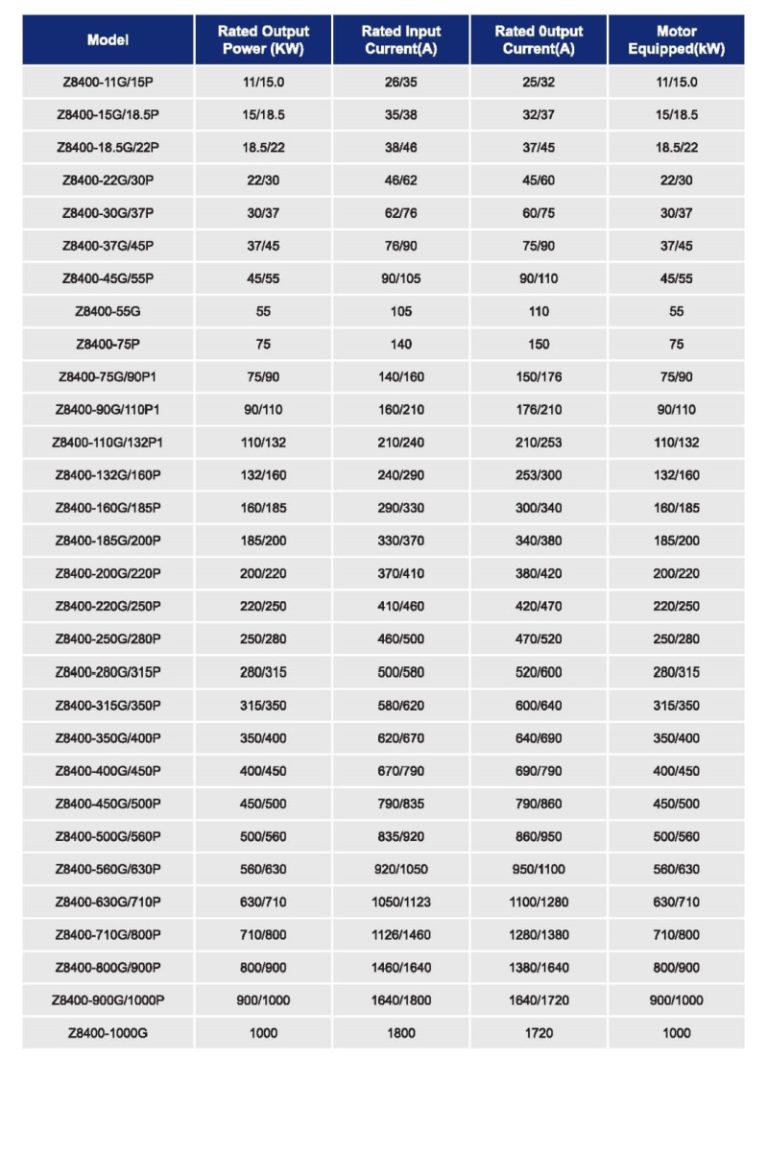
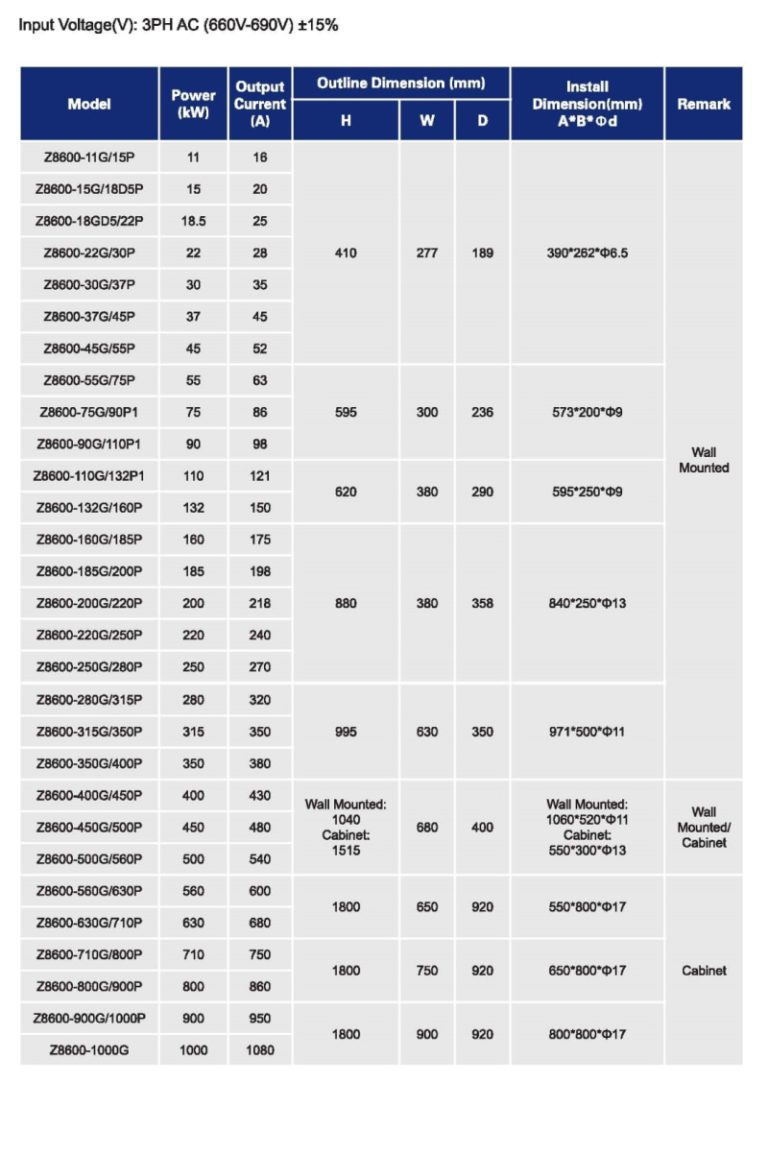
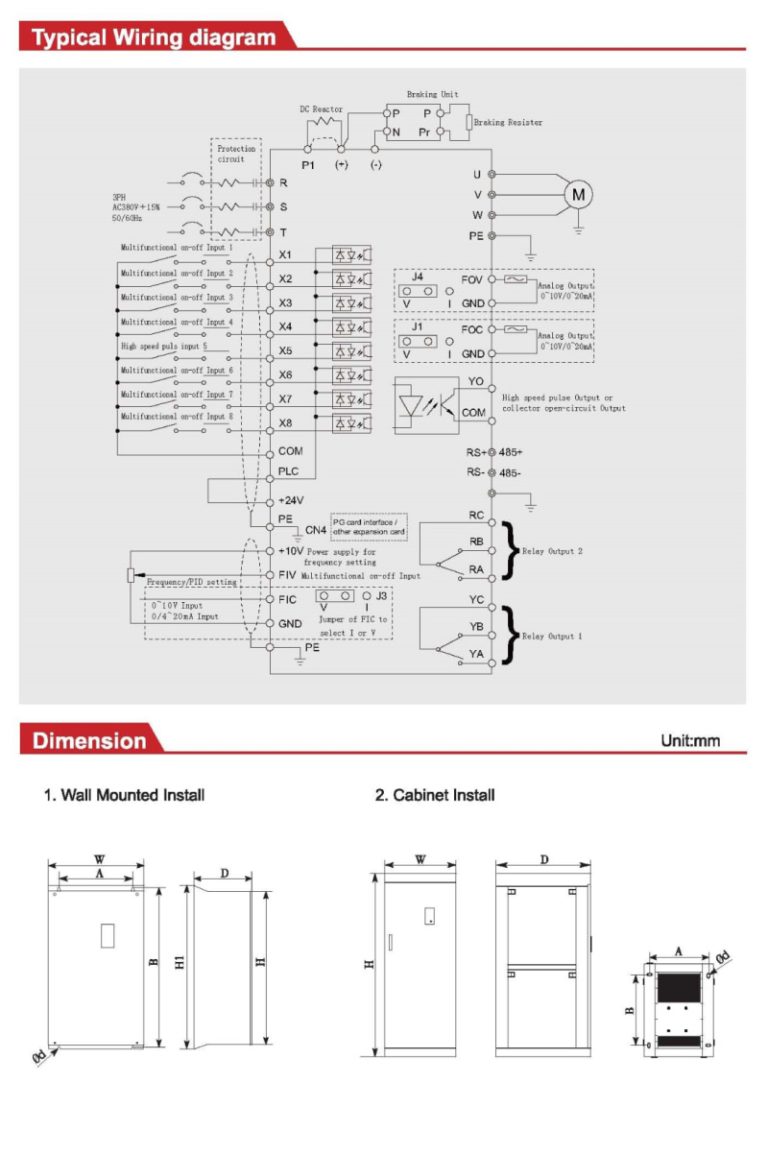
Product description
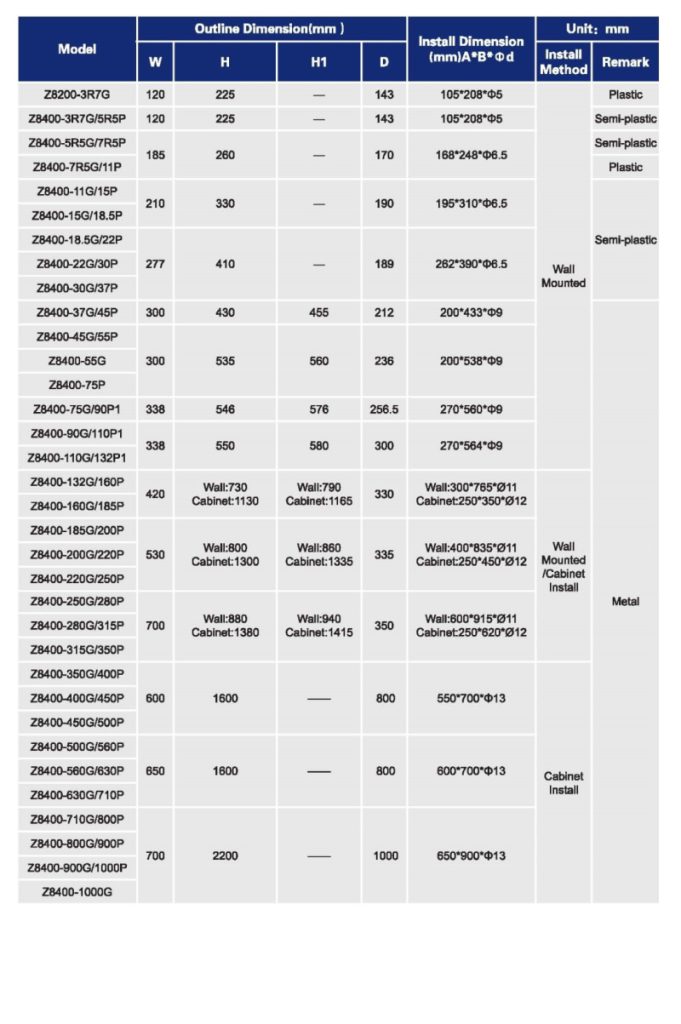
Technical specifications
Control mode Open-loop volume control (without PG), closed-loop volume control (with PG), V/F control
Upper limit frequency Volume control: 0320Hz V/F control: 0~3200Hz
Carrier frequency setting 1kHz~16kHz Carrier frequency can be adjusted automatically according to the load characteristics.
Input frequency resolution Digital setting: 0.01Hz Analogue setting: Maximum frequency × 0.025%.
Starting torque G-type machine: 0.5Hz/150% (without PG); OH/180% (with PG) P-type machine: 0.5H/100
Speed range 1:100 (without PG) 1:1000 (with PG)
Accuracy of speed regulation 0.2% (without PG) ±0.02% (with PG)
Torque control accuracy 5% (with PG)
Overload capacity G-type machine: 150% rated current 60s; 180% rated current 3S P-type machine: 120% rated current 60s; 150% rated current 3s
Torque increase Automatic torque increase; manual torque increase 0.1%~30.0%
VIF curve Three ways: linear; multi-point; N-dimensional V/F curve (1.2-dimensional, 1.4-dimensional, 1.6-dimensional, 1.8-dimensional, 2-dimensional)
VIF separation 2 types: full separation, half separation
Acceleration and deceleration curves Linear or S-curve acceleration and deceleration methods. Four types of acceleration and deceleration time. Acceleration and deceleration time range 0.06500.0S
DC Braking
DC braking frequency: 0.00Hz maximum frequency
Braking time: 0.0S~100.0S
Braking action current value: 0.0% ~ 100.0
Tap control Tap frequency range: 0.00Hz-50.00Hz Tap acceleration and deceleration time 0.0S6500.0S
PLC Multi-Segment Speed Operation Up to 16 segments speed operation can be achieved by built-in PLC or control terminal.
Built-in PID for easy realisation of closed-loop process control systems.
Automatic Voltage Regulation (AVR) Automatically maintains a constant output voltage when the grid voltage changes.
Over-voltage and over-voltage speed control Automatic limitation of current and voltage during operation to prevent frequent over-current and over-voltage tripping.
Fast current limiting function Minimises overcurrent faults and protects the normal operation of the inverter
Torque limiting and control “digger” feature, automatic limitation of torque during operation, preventing frequent overcurrent tripping, closed-loop loss mode can achieve torque control

FAQ
What is a Static Frequency Converter?
A static frequency converter (SFC) is a type of power electronic device used to convert alternating current (AC) of one frequency to alternating current of another frequency. Its main function is to change the frequency of the power supply to suit the needs of different equipment, especially in applications that require a stable, frequency-specific power supply. The main purpose of a static inverter is to enable equipment requiring power at different frequencies to operate seamlessly with the available power supply. In many parts of the world, the standard frequency for AC power distribution is 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the region. However, in some cases, equipment or systems designed for one frequency need to be used in areas with different frequencies. This is where static inverters come into play.
A static inverter is an important power electronic device that is widely used in aviation, marine, power systems and industrial manufacturing. Its main function is to provide a stable, frequency-specific power supply through frequency conversion to meet the special needs of various equipment and systems. Due to its high efficiency, high stability and low maintenance cost, static inverter has an important position in modern industrial and technical applications.


