The process of converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) is called rectification. The main method of rectification is by using a rectifier circuit, which uses semiconductor components (such as diodes) to convert the alternating positive and negative parts of the alternating current into a single direction of current.
What is alternating current?
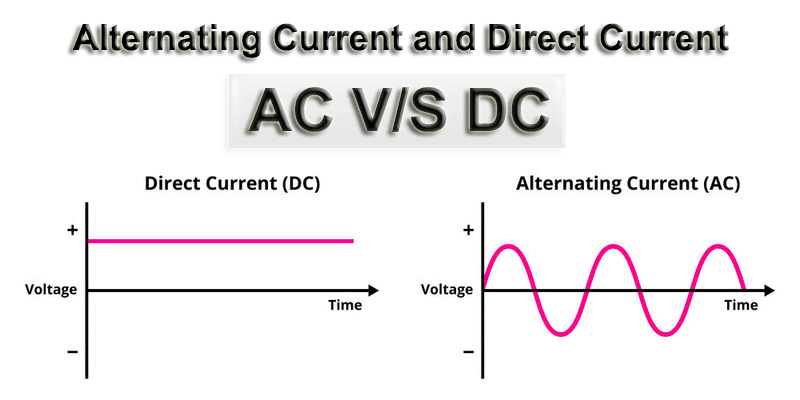
Alternating current (AC) is a form of electricity in which the current constantly changes direction. Alternating current (AC) refers to the flow of electric charge that changes direction periodically. It is the main form of electricity provided by utility companies and used in homes and offices.
Advantages of alternating current:
- 1. Easy to transmit: Since alternating current can be easily stepped up or down by transformers, high voltage can be used to reduce losses during power transmission, making transmission more efficient. Most power transmission and distribution systems use alternating current because it can cover long distances efficiently.
- 2. Easy to convert voltage: Transformers can easily step up or down the voltage of alternating current, allowing the appropriate voltage to be provided according to demand in different application scenarios.
- 3. AC is widely used: Power grids in most countries around the world use alternating current as the standard power supply. Most household appliances, industrial equipment, etc. use AC.
Disadvantages of AC:
Compared with DC, the processing and use of AC requires more complex equipment, such as transformers, voltage regulators, rectifiers, etc. Some electronic devices (such as computers, mobile phones) require stable DC power supply, so AC needs to be rectified to DC.
Application of AC Power:
The power transmission system worldwide is mostly based on AC. Almost all household appliances use AC directly or through adapters.
In industrial equipment, a large number of industrial equipment and machines use AC as a power source.
What is direct current?
Direct current (DC) is a type of electricity that flows in one direction. The current of direct current always flows in the same direction, and the voltage remains constant or changes slowly. Electrochemical cells are typical examples of direct current. It is often used in low-voltage applications such as battery-powered devices, electric vehicles, and electronic products.
Advantages of direct current:
Due to its constant voltage, direct current is suitable for powering electronic devices that require stable voltage power supply. Generally speaking, the circuit design of direct current is relatively simple, easy to control and regulate, especially in small electronic devices. Direct current can be directly used for rechargeable batteries and energy storage devices without conversion losses.
Disadvantages of direct current:
DC is inefficient when transmitted over long distances, has a large voltage drop, high losses, and is difficult to regulate the voltage through a simple transformer. Direct current is prone to arcing when the switch is disconnected, which may cause damage to the switch and contacts. Due to transmission efficiency issues, direct current is usually not used for large-scale power transmission, but is limited to short distances or specific applications.
Applications of direct current:
- Electronic devices: such as mobile phones, laptops, tablets, etc., the internal circuits usually use direct current to work.
- Automotive electrical system: The electrical systems inside the car (such as lights, audio, air conditioning, etc.) mainly use direct current, which is provided by the car battery.
- Power tools: Many portable power tools (such as electric drills and electric saws) are powered by DC batteries, which have the advantage of being easy to move.
Electric vehicles: The power systems of electric vehicles (such as electric cars and electric bicycles) are usually powered by large-capacity DC batteries.
When is AC to DC needed?
In a DC circuit, a stable current flows every time because a DC power supply is provided, while in an AC circuit, the polarity changes at any time because an AC power supply is provided. There are two cycles in an AC circuit: a positive cycle and a negative cycle.
Converting AC to DC is necessary in many applications, especially when a device or system requires a stable supply of voltage and current. The control systems and sensors of many industrial equipment require DC power supply, especially those systems involving precise control and signal processing.
In daily life, we often need AC to DC, such as mobile phone chargers, electric car chargers, rechargeable battery chargers, etc. The charger needs to convert AC to DC suitable for battery charging. This conversion usually includes voltage regulation and control to ensure that the battery is charged safely and efficiently.
How to Convert AC to DC?
The process of converting AC to DC is called rectification. Rectification is usually achieved in several steps:
1. Rectification: Rectification is the conversion of the alternating positive and negative parts of the AC current into a single direction of current.
2. Filtering: Rectified DC is usually still pulsating and is not suitable for directly powering many electronic devices. To obtain smooth DC, filtering is required.
3. Voltage stabilization: Although filtered DC has less fluctuation, it may still cause voltage changes due to load changes or power supply fluctuations. To obtain more stable DC, a voltage stabilizer is required.
4. Output DC: The current that has been rectified, filtered, and stabilized has become smooth, stable DC that can be safely used to power electronic devices. For example, a mobile phone charger converts 220V (or 110V) AC to 5V DC for use in mobile phones.
As our dependence on modern devices and appliances continues to grow, it is important to understand the differences between DC and AC. By skillfully balancing the unique properties of these two powerhouses, performance and energy efficiency are enhanced.

