
There are three powerful types of solar inverters on the market: hybrid, grid-tie, and off-grid inverters. So how much do you know about them?
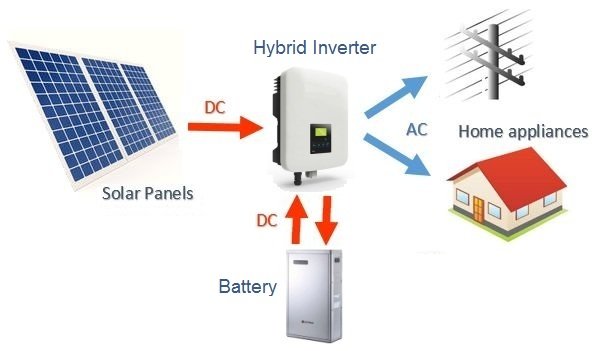
Hybrid solar inverters are devices that combine a solar inverter and a battery inverter into a single unit. This allows the hybrid solar inverter to intelligently handle power from solar panels, solar cells, and the utility grid at the same time.
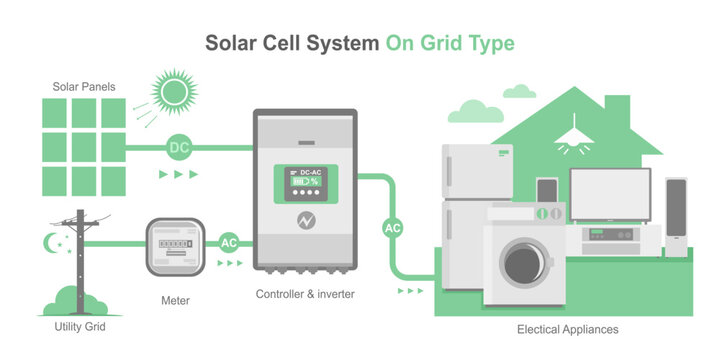
Grid-tie solar inverters, also known as grid-tied or grid-connected systems, are the most commonly used systems for residential and commercial purposes. These systems are directly connected to the local utility grid, allowing users to draw power from the grid when solar panels are unable to generate enough power, such as at night or on cloudy days. Conversely, excess power generated by solar panels can be fed back into the grid. If the utility loses power, a grid-tie solar inverter may not work.
Off-grid solar inverters are not directly connected to the utility grid. Instead, they operate independently. These systems use energy storage solutions such as batteries to store excess power generated when the sun is bright, ensuring continuous power supply on days when the sun is not bright enough. Off-grid systems are not affected by grid failures and ensure continuous power supply even during emergencies or natural disasters. Therefore, off-grid systems are an effective choice for places far from the grid, such as camping areas or picnic spots.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid systems store excess solar power for use at night or during power outages, reducing the need to purchase electricity from the grid, thereby saving electricity bills.
It is compatible with a variety of power sources (such as solar, wind, etc.) and energy storage systems, suitable for different application scenarios.
The only disadvantage of hybrid inverters is that they are expensive to install and take a long time to recover the cost. Installing and maintaining hybrid inverter systems requires a high level of technology, which increases the complexity and maintenance costs of the system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Grid-Connected Inverters
Grid-connected inverters can transmit excess solar power to the grid. By selling excess power back to the grid, users can receive subsidies or benefits, thereby reducing electricity bills. Some homeowners can use this solar system to reduce their monthly bills by more than half.
Although energy storage batteries are not required, the initial investment of grid-connected inverters and solar power generation systems is still high.
If users use a grid-connected system without supplementary power, they may face power outages. At this time, the home inverter may not be able to supply power for several hours.
Grid-tied inverter systems require a sunny location to be installed, so if your home is not in a suitable area, it may be a mistake to use this type of inverter.
After learning so much about solar inverters, have you made a preliminary judgment on how to choose the product? So how to buy a solar inverter?
1. Confirm the location of the house where you install solar energy. We all know that solar inverters mainly obtain energy from the sun, so the location is very important. If your house is located in a sunny area, a grid-connected inverter is a good choice. Otherwise, you can choose the other two types of solar inverters.
2. Verify the budget. For those with a lower budget, you can choose a hybrid solar charger inverter. There are also some local subsidy policies for solar products. You can consult relevant personnel in advance before making a suitable judgment.
Summary
Renewable energy has become increasingly important in our lives. The ability to use the sun to power the entire home is an example that cannot be missed. If you have any needs for inverter products, please contact us at ZONCN. We have the most professional team to help you solve any problems.
By understanding the differences between these solar systems, you can now make your own most informed judgment. Let us make our best contribution to human development and energy conservation.
